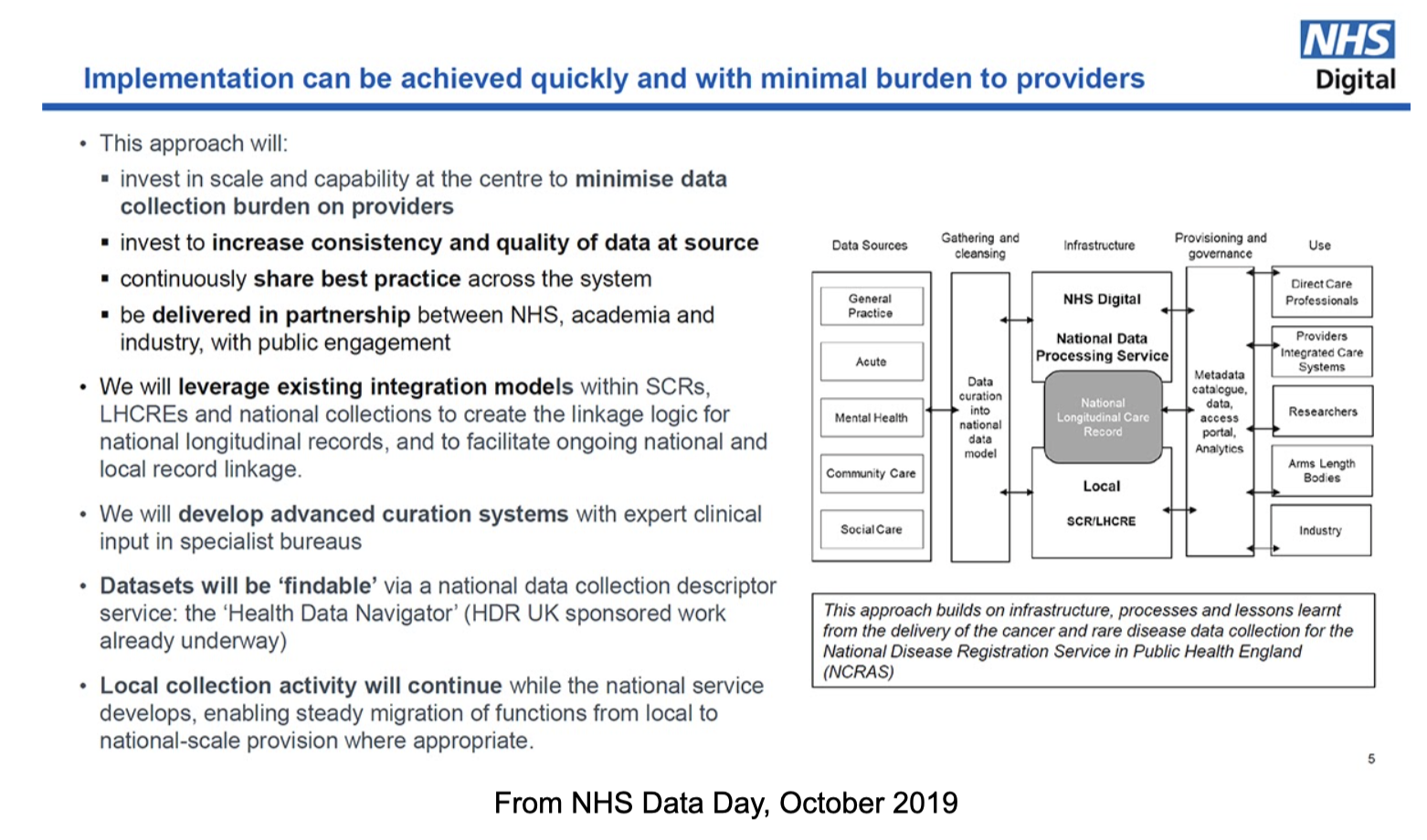
The Goldacre Review is a road map; it is also much more. In many ways it represents an alternative world view to that which is currently being built in ways that have failed at least three times before – not through any lack of political will or even resources, but through a failure of vision.
The choice now facing the country is whether the NHS will fully embrace and build a data infrastructure – which as the Review points out is “code and people with skills”, not beige or black boxes – that is open, collaborative and reproducible or whether, some honourable exceptions aside, it will persist with the status quo of closed, secretive and exploitative data use.
A DHSC-commissioned Review has stated that the dissemination of pseudonymised (i.e. linked and/or linkable, individual-level) patient data is dangerous; something the Government itself acknowledged in Parliament last summer, which this Review has now confirmed.
Professor Goldacre says this is not a “new emergency” – indeed, the practice is endemic – but he is also very clear as to why alarm lights should be flashing. His Review details many of the specifics on pages 85-93.
This is a review of institutional processes, and while it recognises that critical patient-facing aspects of NHS data are damaged and/or unfit for purpose, the Review correctly notes that this is not the place to try to fix them. The NHS has to get its own data house in order before going back to the public.
The success of a review such as this can only be measured by the things that change in the real world as a consequence. Will the research community, the institutions that claim to lead and support that community, and other institutional and corporate users of data now make the necessary changes with the levers available to them?
Open ways of working
The Review describes how open ways of working can be trustworthy and, more importantly, how they can work – but no review can mandate delivery. Nor does it dictate policy.
For example, DHSC has long attempted to “ban” “exclusive” data deals – which the Goldacre Review repeats as expected, while dancing around business models – but both miss the point. Those seeking to use NHS data rarely if ever do so on an “exclusive” basis, not least because it is in the nature of data to be non-rivalrous. What they seek is exclusive control of the insights generated from that data, which contracts entered into by NHS bodies repeatedly sign away.
An “exclusive” deal for data would in practice be harmful only in the context of a single data controller. Even were one hospital to sign up to such “exclusivity” – which as far as we know, none have – then the hospital down the road clearly would not, and should not, be constrained by that exclusivity.
Following previous messes involving, amongst others, Google DeepMind and Sensyne Health plc – none of which prevented those Trusts from cutting other deals with different companies – DHSC told Trusts not to sign ‘naive’ and ‘unsophisticated’ patient data deals and set up the “Centre for Data Expertise”, which has ever since been looking for something to do. The principles of the Goldacre Review should become the core task of that centre – since renamed the “Centre for Improving Data Collaboration” – that is, to assist and guide NHS bodies that are willing to implement open ways of working and the sharing of both code and outputs.
Those who do not wish to modernise, whether they be NHS bodies or HDR UK, can sit on the sidelines and continue to waste public resources they have been given. The Centre, meanwhile, should help those who agree with the Review to implement it faster – including whatever DHSC and NHSEx commissions, and whatever the Service Transformation Directorate prioritises. That assistance should include supporting those who can already build better tools, not just favoured suppliers.
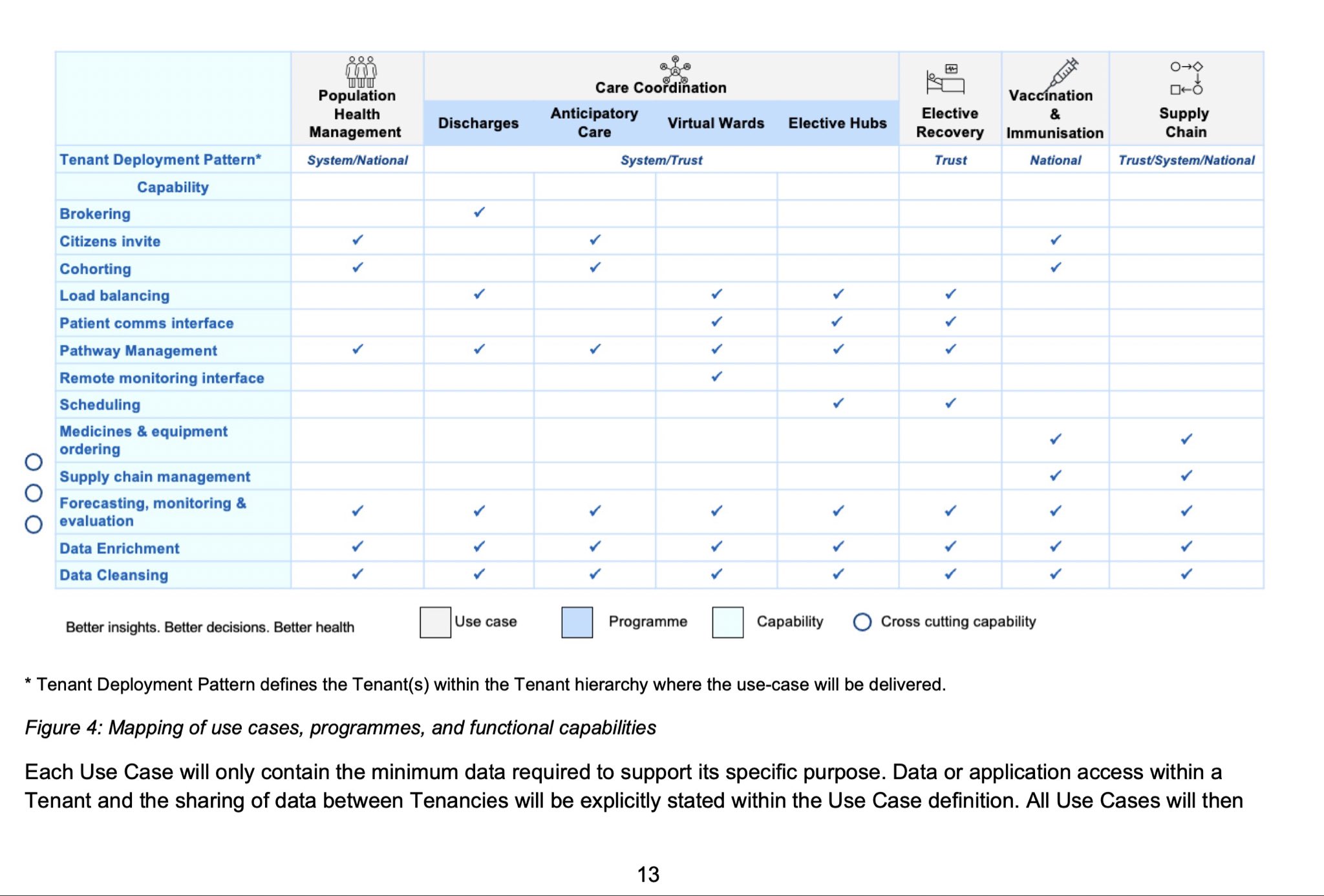
Just as HDIS was for the HES data, there should be similar arrangements for ICSs/ICBs and other geographies so that organisations can see the data they need to see. Some of these views will be from care providers / provider level, and some from higher level aggregators – with commissioners being able to see both the different models for their area, and the models for different interventions.
The abolition of PHE and the move of some public health functions to the NHS should help ease historic turf wars. That this would be useful is demonstrated by the answer to the question, “Is there a public URL where anyone can see, for known defined geographic areas (councils, ICBs, etc.), the current top health issues in those areas, compared with areas nearby?” (The closest answer to which appears to be one blogpost.)
That PHE was unable to publish NHS health measures at the level of CCGs – i.e. where the decisions were made – was not entirely its own fault, but it was never able to do so. In the more open culture of academia, we got openPrescribing for GP prescribing, but even that was limited as it wasn’t able to cover the £7.5 billion spent on hospital medicines.
Safe(r) ways of working
The Review’s call to apply different approval processes according to different data risks is far from unprecedented; ONS has been doing this for many years, for different datasets of different types. This approach has not previously been applied in the NHS, not least because of the acknowledged excessively high risk of giving out full raw datasets to anyone who wants them.
NHS Digital also operates under different constraints, in a different data culture. So while ONS is able to reject access to people it is not assured will follow the rules, NHSD is obliged to supply data to other public bodies which may make their own assurance decisions about their own suppliers, and where governance sanctions are practically non-existent.
There is also something of an obsession with “100%” health datasets, when those producing reliable national statistics know that ‘full coverage’ – such as with the census – is to all intents and purposes the same as a health dataset that has removed the records of every patient who has made a National Data Opt-Out. Indeed, even if NDOO was applied to GP data or hospital data, the remaining data would still have coverage greater than the census.
The suggestion of a ‘one stop’ approval shop is attractive to those who want to water down governance. IGARD and PAG (the BMA and RCGP’s ‘Professional Advisory Group’) have largely worked for GP data, but not entirely – in particular when NHS England “forgot” to inform them of various actions. While a group like PAG minimises the need for every GP to review centralised data extractions and access themselves, the basic principle that any data controller can ‘pull the plug’ is what keeps other parties honest – especially those whose strategic interests mean they are less than completely transparent.
TRE ‘wrappers’
The ONS ‘Five Safes’ model relies on the fact that everyone who comes into the safe setting is already within a trust boundary. Its own processes show that the NHS cannot and does not trust all of the people who would access data, and yet it has to give them data that is intrinsically unsafe.
That NHS England trusts NHS England may be obvious; that’s not to say it is entirely wise. And NHSE’s ‘gatekeeping’ of data research post-merger will likely result in more limitations and rejections of bona fide research, given that in more than a few instances it is likely NHSE won’t like the answers…
Seeing which way the wind is blowing, meanwhile, HDR UK is shovelling money into “sprints” to discover ‘new tech’ for TREs. Its call is flawed and seems designed to to funnel money to incumbents. (That HDR UK wastes UKRI / MRC / ESRC / public funds is not our primary issue of concern. This does matter to all our research friends – but whether the 250+ who signed HDR’s open letter on research access to GP data last summer knew this was what they were signing up to is unclear. HDR did tell them… right?)
HDR UK was designed to build infrastructure. It has failed, and NHS England plans show that the NHS will be the reliable infrastructure provider for NHS data. On UKRI’s proposed budget allocation, MRC / HDR cannot currently afford to continue funding all of the hubs listed in the slide in its latest presentation.
In reality, HDR UK has no framework to maintain infrastructure; it doesn’t know how to build infrastructure that people wish to use; and it doesn’t have any control over the data that can be used. No research programme can have lasting confidence in any research infrastructure provided by HDR or the hubs, for the simple reason that they have defined funding periods and cannot make commitments beyond those periods.
What happens to the next iteration of Farr / HDR UK is up for debate, and we have suggestions of where to start – but whatever it is must be much smaller than the 100+ people at HDR HQ, currently draining resources away from research.
While everyone tries defining “TRE” to mean what they want it to mean, a number of likely models are emerging:
- NHS England: addicted to its COPI powers, Palantir Foundry and dashboards; it may or may not commission its quarter-billion pound ‘Federated Data Platform’ from Palantir – but even if it doesn’t, will this historically closed platform (also) be NHSE’s ‘Planning TRE’? (Noting that, if it does plump for Palantir, NHSE will have the capability to automatically produce Personalised Data Usage Reports for every administrative use of NHS patients’ data by NHSE…)
- OpenSAFELY: currently operating under COPI powers, NHSE’s data controllership and CMO sign-off; a ‘table server’, not a remote-desktop-style setting – but nonetheless a scaleable, safe way to produce non-disclosive results from specified, approved queries run on data in situ. (Could be used almost immediately to reduce burden on other stretched systems, but NHSE is refusing to make any policy decision until it has decided whether to ‘go / no go’ on Palantir.)
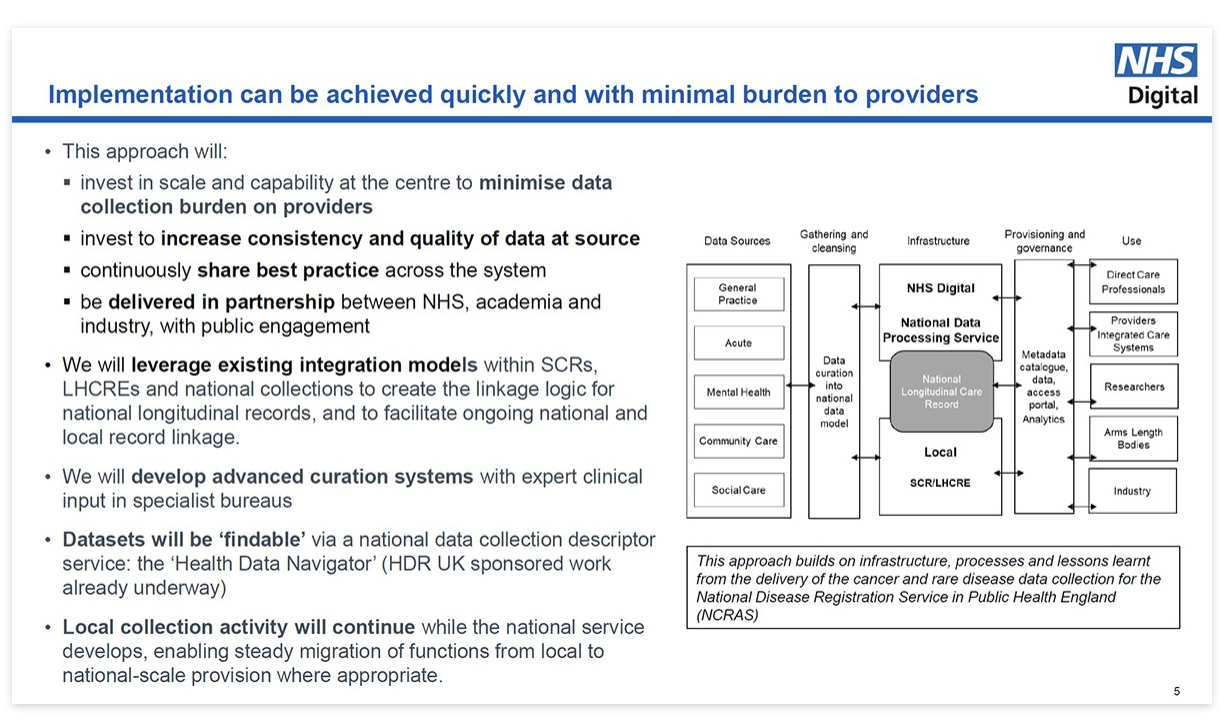
- NHS Digital: has a functioning TRE in which COVID and cancer research is already being done. This TRE is sustainable, its scaling up was funded in March 2022 (amount unknown), and it replicates the ONS model which has been proven to work for researchers and analysts, and whose statistical outputs inform policy and decision makers for years.
- HDR UK: acknowledges it doesn’t have a TRE, but pays to use others’ – mostly NHS Digital’s.
- DHSC / UKHSA’s ‘EDGE’ (now ‘eDAP’?): is described as “near critical national infrastructure” in its tenders, though I bet you’ve never heard of it. It’s not for direct care, so what it does clearly falls under the ‘Research and Planning’ (i.e. secondary) uses about which patients have choices.
- ONS has the Secure Research Service, which already handles mortality data; there’s
SHIP eDRIS in Scotland, and SAIL in Wales; Genomics England Ltd does genomic data; and there’s a proposed National Imaging TRE for training AI models…
Delivering the future
The Goldacre Review recognises, channelling Baroness Onora O’Neill, that the key to the future of health data is trustworthiness.
The merger takeover of the statutorily independent safe haven by NHS England will place the obligations on the public body that is NHS Digital onto NHS England. Some of those obligations are related to use of particular powers, some apply to the public body itself.
DHSC has thus far refused to produce a Keeling Schedule of how Part 9 of HSCA 2012 will look in the statute books when “the Information Centre” is replaced with “NHS England” – we assume because they’ve done the same work we have, and realise how ridiculous it looks. We look forward to seeing how Ministers’ statements at the despatch box will be implemented, if indeed they are even implementable.
NHS England does its own thing because its main job is to ensure there is always someone to blame other than DH and the Secretary of State. DHSC and NHSEx’s shared vision appears limited to “abolish NHS Digital, buy Palantir”, maintaining and expanding closed, secretive and exploitative data use that is not clearly in the public interest.
This latest ‘transformation’ is not just a technical process or platform ‘upgrade’; it’s all about trust and the relationship between a modern, data-competent, data-functional NHS and the people it exists to serve – not the system itself.
We have plenty of evidence on the way officials convince themselves their last mistake was due to factors beyond their control. How they fail to learn lessons, and gradually walk themselves (and others) around in a circle to a new justification of the same old bad decision, with exactly the same goals.
This time, we have to do better.
“No one down here but the NHS’s most unwanted?”
Twitter exhaust suggests the cohort of tech-backgrounds who came into the NHS via NHSX have discovered ‘Seeing Like A State’, and may even be beginning to understand (a little of) why NHSX could not succeed.
Some of the more advanced thinkers may have found Zacka’s ‘When the State Meets the Street’, a tech view of service delivery and moral agency. Moral agency in practice means realising that while those working on AI in NHSX may themselves be well meaning, the DHSC AI lab will always do things that are important to DHSC; that service design at NHS England will always prioritise things that are important to NHS England – and that patients and the NHS frontline lose in both scenarios.
The first Goldacre Review says the data risks are not a “new emergency”, but anyone who reads it will understand why alarm lights should already be flashing. It is likely that ‘Goldacre2’ will have to pick up the pieces where this Review went undelivered, and where the unevidenced assertion of a lack of urgency may have turned out to be overly optimistic.
The success (or not) of Goldacre1 will be measured in the Terms of Reference for Goldacre2.
No-one goes to work in the morning to be transformed; those who go to work to help people especially not. Matt Hancock appeared to understand this when he came up with the idea of an NHSX ‘with vision’, in ways that NHS England clearly didn’t when setting up the (National Health) Service Transformation Directorate – which in many ways is still Hancock’s Service Transformation Directorate, albeit without as much interest from political leadership.
No longer named like the popular TV show from Matt Hancock’s youth, the STD risks replicating Mulder’s opening line from the X-Files. Goldacre1 could actually make it useful. It’s a vision thing.
Coverage of flying saucers and Nessie largely went away once we got good camera phones; data headlines should go away when the NHS gets open methods and reproducible analytics, all running in TREs. Any dashboard needed at any level of the system can be run that way.
The NHS is currently making a choice – or, more accurately, appears to be trying to rationalise choices it has already made – between investing in genuinely open, collaborative and reproducible data for planning and research, as laid out by the Goldacre Review, or persisting and spreading the status quo of closed, secretive and exploitative data use that is so toxic to trust.
Which is not what anyone wants.
Enc docs: